GCC__attribute__部分使用方法
GNU __attribute__(())部分使用方法
一部分
自定义段(将全局变量或函数放入自定义的段)
例如:linux内核
__init__#define __init__ __attribute__((section(".init")))3种写法都可以
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16#include <stdio.h>
#define ps(str) printf("%s",str)
int global __attribute__((section(".Data"))) = 42;
__attribute__((section(".test"))) int b = 9;
int __attribute__((section(".test2"))) c = 8;
__attribute__((section(".func")))
void globalfunc() {}
int main()
{
return 0;
}gcc -c test.c查看
test.o的sectionreadeld -a test.o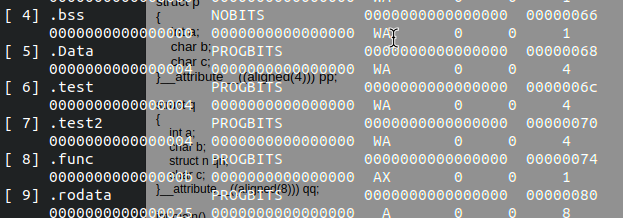
constructor/destructor属性,如果函数设置constructor属性则在main()之前被执行,destructor同理1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21#include <stdio.h>
#define ps(str) printf("%s\n",str)
__attribute__((constructor))
void constructor()
{
ps("constructor");
}
__attribute__((destructor))
void destructor()
{
ps("destructor");
}
int main()
{
ps("begin");
ps("end");
return 0;
}属性写在返回类型前也可以
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19#include <stdio.h>
#define ps(str) printf("%s\n",str)
void __attribute__((constructor)) constructor()
{
ps("constructor");
}
void __attribute__((destructor)) destructor()
{
ps("destructor");
}
int main()
{
ps("begin");
ps("end");
return 0;
}cleanup()属性修饰变量,在其作用域结束时执行指定函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25#include <stdio.h>
#define ps(str) printf("%s\n",str)
#define pd(d) printf("%d\n",d);
void clean()
{
ps("变量作用域结束的清理函数");
}
struct A
{
int a;
int b;
};
int main()
{
ps("begin");
{
int b __attribute__((cleanup(clean))) = 1;
struct A c __attribute__((cleanup(clean))) = {1,2};
}
ps("end");
return 0;
}
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-SA 4.0 协议 ,转载请注明出处!